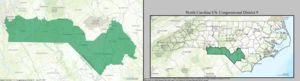
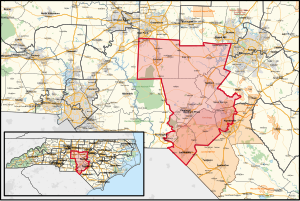
North Carolina's 9th congressional district
| North Carolina's 9th congressional district | |
|---|---|
Interactive map of district boundaries since January 3, 2025 | |
| Representative | |
| Population (2023) | 771,994[1] |
| Median household income | $64,306[1] |
| Ethnicity |
|
| Cook PVI | R+6[2] |
North Carolina's 9th congressional district is a congressional district in south-central North Carolina. The district's current boundaries were redrawn in February 2016 after a U.S. District Court overturned the existing boundaries because of politically directed gerrymandering that suppressed minority representation.[3][4] The new congressional district consists of Union, Chatham, Anson, Richmond, Scotland, and Robeson counties; a southeast portion of Mecklenburg County; and parts of Cumberland, Moore and Bladen counties.
Republicans have held this district since 1963. Republican Robert Pittenger had represented the district since January 2013. In 2018, Pittenger was defeated by challenger Mark Harris in the Republican primary. The latter faced Democrat Dan McCready in the general election.
Harris was initially called as the winner by several hundred votes, but the result was not certified, pending a statewide investigation into allegations of absentee ballot fraud.[5][6] On February 21, the bipartisan State Election Board unanimously voted to call for a new election for the 9th district, because of ballot fraud by Republican operatives.[7]
A special election was held September 10, 2019, with Democrat Dan McCready running against Republican Dan Bishop, a state senator who won the Republican primary.[8] Bishop won the 2019 special election to the U.S. House of Representatives with 50.7% of the vote to McCready's 48.7%.[9][10]
Candidate filing began February 24, 2022 after the North Carolina Supreme Court approved a new map which changed the 9th district boundaries to include Chatham, Hoke, Lee, Moore, Randolph and Scotland Counties and parts of Cumberland, Harnett and Richmond Counties.[11]
The ninth district is currently represented by Richard Hudson.
Counties
[edit]Counties in the 2023–2025 district map:
- Chatham County
- Cumberland County (part)
- Harnett County (part)
- Hoke County
- Lee County
- Moore County
- Randolph County
- Richmond County (part)
- Scotland County
Recent election results from statewide races
[edit]| Year | Office | Results[12] |
|---|---|---|
| 2008 | President | McCain 54% - 44% |
| 2012 | President | Romney 57% - 43% |
| 2014 | Senate | Tillis 56% - 40% |
| 2016 | President | Trump 57% - 40% |
| Senate | Burr 57% - 39% | |
| Governor | McCrory 55% - 43% | |
| Lt. Governor | Forest 58% - 39% | |
| Attorney General | Newton 56% - 44% | |
| 2020 | President | Trump 56% - 42% |
| Senate | Tillis 54% - 41% | |
| Governor | Forest 52% - 46% | |
| Lt. Governor | Robinson 58% - 42% | |
| Secretary of State | Sykes 55% - 45% | |
| Auditor | Street 55% - 45% | |
| Attorney General | O'Neill 56% - 44% | |
| Treasurer | Folwell 58% - 42% | |
| 2022 | Senate | Budd 58% - 40% |
List of members representing the district
[edit]2018 Voter Fraud
[edit]In the Republican primary incumbent Robert Pittenger was defeated by former pastor Mark Harris, who had closely challenged him two years earlier.[15] Harris won 48.5 percent of the vote to Pittenger's 46.2 percent.[16]
The New York Times described the election between Harris and Democrat Dan McCready as a "top-tier contest".[17] In results on election day, Harris defeated McCready by 905 votes, but on November 27, 2018, the North Carolina State Board of Elections and Ethics Reform declined to certify the election results, citing voting irregularities involving absentee ballots.[18][19] The irregularities in counting and handling of absentee ballots became the subject of a criminal investigation.[20]
Outlets such as the Associated Press[21] and FiveThirtyEight[22] subsequently retracted calling the race, pending the decision of the state board of elections. On December 1, the chair of the state elections board resigned, saying: "The investigation of criminal conduct and absentee voting fraud in the 2018 Republican primary and 2018 general election in congressional district 9 is a matter of vital importance to our democracy", adding that "I will not allow myself to be used as an instrument of distraction in this investigation".[23]
On November 30, the election board of the district decided to hear evidence about "claims of numerous irregularities and concerted fraudulent activities" at a meeting to be held by December 21. A finding of fraud could have resulted in a new election.[24]
On December 5, 2018, independent investigative reporting of the alleged vote thefts detailed a practice that targeted southern rural elderly black voters in the 9th district congressional race and termed the affair, "...the most serious federal election tampering case in years." Campaign workers revealed that the vote tampering went on in a pervasively chaotic atmosphere. Operatives tracked votes and field workers "...would come to your house, they would get you to fill out an absentee ballot to be sent to your house. They would go back and pick it up and then seal it and then find two witnesses," to certify their validity. Such handling of ballots and completed applications by other than board and postal workers is legally prohibited. An informant tabulated the number of ballots delivered to the county election board and said an indicted leader gave the Harris campaign updates on the operation's most recent totals. The leader was employed by Red Dome political consultants which received over $428,000 from the Harris campaign. The informant had delivered 185 absentee ballot applications and the leader personally delivered 592 more.[25] On December 6, Democratic candidate McCready withdrew his earlier submitted election concession.[26] Republican candidate Harris agreed for a new election to be held if allegations of election fraud could be proven by the election board to have affected the contest's outcome.[27] The leader of the North Carolina Republicans, Robin Hayes, stated on December 11 that, regardless to what extent election fraud could be proven to have altered the election, a new election would be necessary in the state's 9th congressional district if investigators can verify a local newspaper report that early voting results in Bladen County were leaked before Election Day.[28][29]
On December 28, the state court dissolved the state election board, before it had certified election results.[30][31] The election board's staff announced that it would continue the investigation, but delayed hearings until a new election board was seated, presumably on January 31.[32][33] Democratic Governor Roy Cooper's attempts to fill an interim board were overridden by the Republican-controlled legislature.[30] Incoming United States House of Representatives Majority Leader Steny Hoyer, a Democrat, announced that the House of Representatives would not seat Harris under any circumstances until the fraud investigation is completed.[34] Harris announced he would seek court intervention to have him immediately certified as the winner and stated his intention to join the 116th Congress on January 3.[35][36] However, Harris was not permitted to join the new Congress on January 3.
On February 21, the bipartisan state board of elections voted to hold a new election, because, according to board chairman Bob Cordle, "irregularities and improprieties ... tainted the results ... and cast doubt on its fairness."[37] A newly passed law by the North Carolina state legislature will require the parties to hold new primaries before the general election for this seat.[38][39][40][41] Harris has said that he will not run again.
2019 special election
[edit]Democrat Dan McCready, a veteran and business executive, was unopposed as his party's nominee for this seat, following his narrow initial loss to Mark Harris in the election voided because of alleged ballot fraud by Republican operatives. After the Republicans conducted their primary, they nominated Dan Bishop, a North Carolina state senator, to run in the special election to be held in September 2019.[8] On September 10, 2019, Bishop narrowly won the election with 50.7% of the vote to McCready's 48.7%.[9][42] He was sworn in on September 17, 2019.[43]
Past election results
[edit]2012
[edit]| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Robert Pittenger | 194,537 | 51.8 | |
| Democratic | Jennifer Roberts | 171,503 | 45.6 | |
| Libertarian | Curtis Campbell | 9,650 | 2.6 | |
| Total votes | 375,690 | 100.0 | ||
| Republican hold | ||||
2014
[edit]| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Robert Pittenger (incumbent) | 163,080 | 93.9 | |
| N/A | Write-ins | 8,219 | 4.7 | |
| Independent | Shawn Eckles (write-in) | 2,369 | 1.4 | |
| Total votes | 173,668 | 100.0 | ||
| Republican hold | ||||
2016
[edit]| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Robert Pittenger (incumbent) | 193,452 | 58.2 | |
| Democratic | Christian Cano | 139,041 | 41.8 | |
| Total votes | 332,493 | 100.0 | ||
| Republican hold | ||||
2018
[edit]| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Mark Harris | 139,246 | 49.25 | |
| Democratic | Dan McCready | 138,341 | 48.93 | |
| Libertarian | Jeff Scott | 5,130 | 1.81 | |
| Total votes | 282,717 | 100.0 | ||
| Republican hold | ||||
2019 special election
[edit]| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Dan Bishop | 96,573 | 50.69 | |
| Democratic | Dan McCready | 92,785 | 48.70 | |
| Libertarian | Jeff Scott | 773 | 0.41 | |
| Green | Allen Smith | 375 | 0.20 | |
| Total votes | 190,506 | 100.00 | ||
| Republican hold | ||||
2020
[edit]| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Dan Bishop (incumbent) | 224,661 | 55.6 | |
| Democratic | Cynthia Wallace | 179,463 | 44.4 | |
| Total votes | 404,124 | 100.0 | ||
| Republican hold | ||||
2022
[edit]| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Richard Hudson (incumbent) | 131,453 | 56.50 | ||
| Democratic | Ben Clark | 101,202 | 43.50 | ||
| Total votes | 232,655 | 100.00 | |||
| Republican hold | |||||
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ Supported the Crawford faction in the 1824 United States presidential election.
- ^ Election voided by the North Carolina State Board of Elections due to election fraud.[48]
References
[edit]- ^ a b "My Congressional District". census.gov. U.S. Census Bureau Center for New Media and Promotion (CNMP).
- ^ "2022 Cook PVI: District Map and List". Cook Political Report. Retrieved January 10, 2023.
- ^ "Session Law 2016-1". Retrieved May 30, 2016.
- ^ "Congressional Districts Relationship Files (state-based)". www.census.gov. U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved April 9, 2018.
- ^ Morrill, Jim (November 27, 2018). "NC elections board refuses to certify 9th District race, leaving it in limbo". Charlotte Observer. Retrieved November 28, 2018.
- ^ Bock Clark, Doug (December 2, 2018). "Allegations of G.O.P. Election Fraud Shake North Carolina's Ninth District". The New Yorker. New York City, N.Y. Retrieved December 3, 2018.
- ^ "Mark Harris calls for new election in 9th district". newsobserver. Retrieved February 21, 2019.
- ^ a b Sonmez, Felicia; Gardner, Amy (May 14, 2019). "Republican voters nominate N.C. state lawmaker who sponsored controversial 'bathroom bill' in 9th Congressional District race". Washington Post. Retrieved May 19, 2019.
- ^ a b Live results: North Carolina elections, Politico, September 10, 2019.
- ^ Republican Dan Bishop wins special election for House seat in North Carolina special election, NBC News projects, NBC News, September 10, 2019.
- ^ Battaglia, Danielle (February 24, 2022). "NC member of Congress announces where he'll run, a day after floating other options". The Charlotte Observer. Retrieved March 21, 2022.
- ^ https://davesredistricting.org/maps#viewmap::4f133eac-adb1-4bb4-a7fe-92aa8a5f1ed4
- ^ a b c d "Data Courtesy of Jeffrey B. Lewis, Brandon DeVine, and Lincoln Pritcher with Kenneth C. Martis". United States Congressional District Shapefiles.
- ^ "New election ordered in North Carolina House district after possible illegal activities". NBC News. Retrieved February 22, 2019.
- ^ Morrill, Jim (May 8, 2018). "Challenger Mark Harris stuns U.S. Rep. Pittenger of NC in GOP primary upset". Charlotte Observer. Charlotte, N.C. Retrieved May 12, 2018.
- ^ Weigel, David (May 8, 2018). "North Carolina GOP congressman loses primary, first House incumbent ousted". Washington Post. Retrieved May 12, 2018.
- ^ Buchanan, Larry; Bloch, Matthew; Bowers, Jeremy; Cohn, Nate; Coote, Alastair; Daniel, Annie; Harris, Richard; Katz, Josh; Lieberman, Rebecca; Migliozzi, Blacki; Murray, Paul; Pearce, Adam; Quealy, Kevin; Weingart, Eden; White, Isaac (October 2018). "We polled voters in North Carolina's 9th Congressional District". The New York Times. Retrieved October 23, 2018.
- ^ Morrill, Jim (November 29, 2018). "'Tangled web' in Bladen County has questions swirling about votes in the 9th District". The Charlotte Observer. Charlotte, North Carolina. Retrieved November 30, 2018.
- ^ Gardner, Amy; Ross, Kirk (November 29, 2018). "Certification in limbo in N.C. House race as fraud investigation continues". The Washington Post. Washington, D.C. Retrieved November 30, 2018.
- ^ Durkin, Erin (December 5, 2018). "North Carolina election still undecided amid absentee ballot fraud inquiry" – via www.theguardian.com.
- ^ "The Latest: AP Retracts call in North Carolina Congress race". AP. November 30, 2018. Retrieved December 1, 2018.
- ^ Rakich, Nathaniel (November 30, 2018). "What The Heck Is Happening In That North Carolina House Race?". FiveThirtyEight. Retrieved December 1, 2018.
- ^ Gardner, Amy (December 1, 2018). "North Carolina elections board chairman resigns, says he doesn't want his partisan views to hurt election fraud investigation". The Washington Post. Washington, D.C. Archived from the original on December 2, 2018. Retrieved December 1, 2018.
- ^ Bock Clark, Doug (December 2, 2018). "Allegations of G.O.P. Election Fraud Shake North Carolina's Ninth District". The New Yorker. New York. Retrieved December 9, 2018.
- ^ Inside The North Carolina Republican Vote Machine: Cash, Pills — And Ballots, Buzzfeed News, Brianna Sacks and Otillia Steadman, December 5, 2018. Retrieved August 5, 2019.
- ^ "North Carolina: Democrat withdraws concession in congressional race". The Guardian. Associated Press. December 7, 2018. Retrieved December 9, 2018.
- ^ Bump, Philip (December 10, 2018). "Why fraud allegations throw the results in North Carolina's 9th District into doubt". The Washington Post. Washington D.C. Retrieved December 11, 2018.
- ^ Way, Dan (December 11, 2018). "NCGOP preparing to call for new election in 9th District". Carolina Journal. Raleigh, North Carolina. Retrieved December 13, 2018.
- ^ Nobles, Ryan (December 13, 2018). "Will Republicans abandon their candidate in North Carolina's 9th Congressional District?". CNN. Retrieved December 13, 2018.
- ^ a b Henderson, Bruce; Jarvis, Craig; Brosseau, Carli (December 28, 2018). "9th District chaos: Cooper plans interim elections board, Harris asks to be named winner". The Charlotte Observer. Retrieved January 3, 2019.
- ^ Nobles, Ryan; Krieg, Gregory; Stracqualursi, Veronica; Cohen, Ethan (December 28, 2018). "North Carolina elections board dissolves before certifying November results of 9th district race". CNN. Archived from the original on January 3, 2019. Retrieved January 3, 2019.
- ^ Dalesio, Emery P. (January 2, 2019). "Hearing into North Carolina ballot fraud claims postponed". The Charlotte Observer. Archived from the original on January 3, 2019. Retrieved January 3, 2019.
- ^ "Hearing On 9th District Investigation Delayed". WFAE. January 2, 2019. Archived from the original on January 3, 2019. Retrieved January 3, 2019.
- ^ "House leader says Democrats won't seat candidate in unresolved North Carolina race". AP via NBC News. December 28, 2018. Archived from the original on January 3, 2019. Retrieved January 3, 2019.
- ^ Gardner, Amy (January 2, 2019). "GOP congressional candidate says he will ask N.C. court to certify his victory as election officials delay fraud hearing". The Washington Post. Retrieved January 3, 2019.
- ^ Morrill, Jim; Murphy, Brian (January 2, 2019). "Mark Harris says he'll go to court as officials delay hearing on election fraud". The Charlotte Observer. Retrieved January 3, 2019.
- ^ Gardner, Amy (February 21, 2019). "N.C. board declares a new election in contested House race after the GOP candidate admitted misspeaking under oath". The Washington Post. Retrieved February 21, 2019.
- ^ "North Carolina lawmakers override veto of elections bill". TheHill. December 27, 2018. Retrieved December 30, 2018.
- ^ Williams, Timothy (December 12, 2018). "North Carolina Legislature Calls for New Primary if New Election Is Held in Disputed District". The New York Times. New York. Retrieved December 13, 2018.
- ^ Bruno, Joe (December 13, 2018). "Amid fraud probe, an election redo might require new primary for 9th District". WSOC-TV. Charlotte, N.C. Retrieved December 13, 2018.
- ^ Harrison, Steve (December 13, 2018). "Latest On 9th Congressional District Fraud Allegations". WFAE 90.7 Charlotte's NPR News Source. Charlotte, N.C. Retrieved December 13, 2018.
- ^ Taylor, Jessica (September 10, 2019). "Republican Dan Bishop Wins North Carolina Special Congressional Election". NPR. Retrieved October 2, 2020.
- ^ Midura, Kyle (September 17, 2019). "Dan Bishop sworn into Congress in Washington, D.C." WBTV. Gray DC Bureau. Retrieved October 2, 2020.
- ^ "North Carolina General Elections Results 2012". North Carolina State Board of Elections. Retrieved January 22, 2013.
- ^ "North Carolina Official General Election Results". North Carolina State Board of Elections. November 4, 2014. Archived from the original on January 27, 2015. Retrieved January 23, 2015.
- ^ "North Carolina Official General Election Results". North Carolina State Board of Elections. November 8, 2016. Retrieved January 3, 2017.
- ^ "District 9, North Carolina State Board of Elections & Ethics Enforcement". North Carolina State Board of Elections & Ethics Enforcement. Retrieved November 10, 2018.
- ^ Steinmetz, Jesse (November 16, 2021). "Reporters detail NC's infamous 2018 race for the 9th Congressional District in 'The Vote Collectors'". WFAE 90.7. Retrieved August 10, 2023.
- ^ "US HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES DISTRICT 09 - REP (VOTE FOR 1)". NC State Board of Elections. Retrieved September 15, 2019.
- ^ "State Composite Abstract Report - Contest.pdf" (PDF). North Carolina State Board of Elections. Retrieved November 24, 2020.
- ^ "NC SBE Contest Results". er.ncsbe.gov. Retrieved January 2, 2023.
- Martis, Kenneth C. (1989). The Historical Atlas of Political Parties in the United States Congress. New York: Macmillan Publishing Company.
- Martis, Kenneth C. (1982). The Historical Atlas of United States Congressional Districts. New York: Macmillan Publishing Company.
- Congressional Biographical Directory of the United States 1774–present