Coal
| Sedimentary rock | |
 Bituminous coal, the most common coal grade | |
| Composition | |
|---|---|
| Primary | carbon |
| Secondary | |
| Part of a series on |
| Coal |
|---|
 |
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.[1] Coal is a type of fossil fuel, formed when dead plant matter decays into peat which is converted into coal by the heat and pressure of deep burial over millions of years.[2] Vast deposits of coal originate in former wetlands called coal forests that covered much of the Earth's tropical land areas during the late Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) and Permian times.[3][4]
Coal is used primarily as a fuel. While coal has been known and used for thousands of years, its usage was limited until the Industrial Revolution. With the invention of the steam engine, coal consumption increased.[5] In 2020, coal supplied about a quarter of the world's primary energy and over a third of its electricity.[6] Some iron and steel-making and other industrial processes burn coal.
The extraction and burning of coal damages the environment, causing premature death and illness,[7] and it is the largest anthropogenic source of carbon dioxide contributing to climate change. Fourteen billion tonnes of carbon dioxide were emitted by burning coal in 2020,[8] which is 40% of total fossil fuel emissions[9] and over 25% of total global greenhouse gas emissions.[10] As part of worldwide energy transition, many countries have reduced or eliminated their use of coal power.[11][12] The United Nations Secretary General asked governments to stop building new coal plants by 2020.[13]
Global coal use was 8.3 billion tonnes in 2022,[14] and is set to remain at record levels in 2023.[15] To meet the Paris Agreement target of keeping global warming below 2 °C (3.6 °F) coal use needs to halve from 2020 to 2030,[16] and "phasing down" coal was agreed upon in the Glasgow Climate Pact.
The largest consumer and importer of coal in 2020 was China, which accounts for almost half the world's annual coal production, followed by India with about a tenth. Indonesia and Australia export the most, followed by Russia.[17][18]
Etymology
The word originally took the form col in Old English, from reconstructed Proto-Germanic *kula(n), from Proto-Indo-European root *g(e)u-lo- "live coal".[19] Germanic cognates include the Old Frisian kole, Middle Dutch cole, Dutch kool, Old High German chol, German Kohle and Old Norse kol. Irish gual is also a cognate via the Indo-European root.[19]
Formation of coal

The conversion of dead vegetation into coal is called coalification. At various times in the geologic past, the Earth had dense forests[20] in low-lying areas. In these wetlands, the process of coalification began when dead plant matter was protected from oxidation, usually by mud or acidic water, and was converted into peat. The resulting peat bogs, which trapped immense amounts of carbon, were eventually deeply buried by sediments. Then, over millions of years, the heat and pressure of deep burial caused the loss of water, methane and carbon dioxide and increased the proportion of carbon.[21] The grade of coal produced depended on the maximum pressure and temperature reached, with lignite (also called "brown coal") produced under relatively mild conditions, and sub-bituminous coal, bituminous coal, or anthracite coal (also called "hard coal" or "black coal") produced in turn with increasing temperature and pressure.[2][22]
Of the factors involved in coalification, temperature is much more important than either pressure or time of burial.[23] Subbituminous coal can form at temperatures as low as 35 to 80 °C (95 to 176 °F) while anthracite requires a temperature of at least 180 to 245 °C (356 to 473 °F).[24]
Although coal is known from most geologic periods, 90% of all coal beds were deposited in the Carboniferous and Permian periods.[25] Paradoxically, this was during the Late Paleozoic icehouse, a time of global glaciation. However, the drop in global sea level accompanying the glaciation exposed continental shelves that had previously been submerged, and to these were added wide river deltas produced by increased erosion due to the drop in base level. These widespread areas of wetlands provided ideal conditions for coal formation.[26] The rapid formation of coal ended with the coal gap in the Permian–Triassic extinction event, where coal is rare.[27]
Favorable geography alone does not explain the extensive Carboniferous coal beds.[28] Other factors contributing to rapid coal deposition were high oxygen levels, above 30%, that promoted intense wildfires and formation of charcoal that was all but indigestible by decomposing organisms; high carbon dioxide levels that promoted plant growth; and the nature of Carboniferous forests, which included lycophyte trees whose determinate growth meant that carbon was not tied up in heartwood of living trees for long periods.[29]
One theory suggested that about 360 million years ago, some plants evolved the ability to produce lignin, a complex polymer that made their cellulose stems much harder and more woody. The ability to produce lignin led to the evolution of the first trees. But bacteria and fungi did not immediately evolve the ability to decompose lignin, so the wood did not fully decay but became buried under sediment, eventually turning into coal. About 300 million years ago, mushrooms and other fungi developed this ability, ending the main coal-formation period of earth's history.[30][31][32] Although some authors pointed at some evidence of lignin degradation during the Carboniferous, and suggested that climatic and tectonic factors were a more plausible explanation,[33] reconstruction of ancestral enzymes by phylogenetic analysis corroborated a hypothesis that lignin degrading enzymes appeared in fungi approximately 200 MYa.[34]
One likely tectonic factor was the Central Pangean Mountains, an enormous range running along the equator that reached its greatest elevation near this time. Climate modeling suggests that the Central Pangean Mountains contributed to the deposition of vast quantities of coal in the late Carboniferous. The mountains created an area of year-round heavy precipitation, with no dry season typical of a monsoon climate. This is necessary for the preservation of peat in coal swamps.[35]
Coal is known from Precambrian strata, which predate land plants. This coal is presumed to have originated from residues of algae.[36][37]
Sometimes coal seams (also known as coal beds) are interbedded with other sediments in a cyclothem. Cyclothems are thought to have their origin in glacial cycles that produced fluctuations in sea level, which alternately exposed and then flooded large areas of continental shelf.[38]
Chemistry of coalification
The woody tissue of plants is composed mainly of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin. Modern peat is mostly lignin, with a content of cellulose and hemicellulose ranging from 5% to 40%. Various other organic compounds, such as waxes and nitrogen- and sulfur-containing compounds, are also present.[39] Lignin has a weight composition of about 54% carbon, 6% hydrogen, and 30% oxygen, while cellulose has a weight composition of about 44% carbon, 6% hydrogen, and 49% oxygen. Bituminous coal has a composition of about 84.4% carbon, 5.4% hydrogen, 6.7% oxygen, 1.7% nitrogen, and 1.8% sulfur, on a weight basis.[40] The low oxygen content of coal shows that coalification removed most of the oxygen and much of the hydrogen a process called carbonization.[41]
Carbonization proceeds primarily by dehydration, decarboxylation, and demethanation. Dehydration removes water molecules from the maturing coal via reactions such as[42]
- 2 R–OH → R–O–R + H2O
Decarboxylation removes carbon dioxide from the maturing coal:[42]
- RCOOH → RH + CO2
while demethanation proceeds by reaction such as
- 2 R-CH3 → R-CH2-R + CH4
- R-CH2-CH2-CH2-R → R-CH=CH-R + CH4
In these formulas, R represents the remainder of a cellulose or lignin molecule to which the reacting groups are attached.
Dehydration and decarboxylation take place early in coalification, while demethanation begins only after the coal has already reached bituminous rank.[43] The effect of decarboxylation is to reduce the percentage of oxygen, while demethanation reduces the percentage of hydrogen. Dehydration does both, and (together with demethanation) reduces the saturation of the carbon backbone (increasing the number of double bonds between carbon).
As carbonization proceeds, aliphatic compounds convert to aromatic compounds. Similarly, aromatic rings fuse into polyaromatic compounds (linked rings of carbon atoms).[44] The structure increasingly resembles graphene, the structural element of graphite.
Chemical changes are accompanied by physical changes, such as decrease in average pore size.[45]
Macerals
Macerals are coalified plant parts that retain the morphology and some properties of the original plant. In many coals, individual macerals can be identified visually. Some macerals include:[46]
- vitrinite, derived from woody parts
- lipinite, derived from spores and algae
- inertite, derived from woody parts that had been burnt in prehistoric times
- huminite, a precursor to vitrinite.
In coalification huminite is replaced by vitreous (shiny) vitrinite.[47] Maturation of bituminous coal is characterized by bitumenization, in which part of the coal is converted to bitumen, a hydrocarbon-rich gel.[48] Maturation to anthracite is characterized by debitumenization (from demethanation) and the increasing tendency of the anthracite to break with a conchoidal fracture, similar to the way thick glass breaks.[49]
Types


As geological processes apply pressure to dead biotic material over time, under suitable conditions, its metamorphic grade or rank increases successively into:
- Peat, a precursor of coal
- Lignite, or brown coal, the lowest rank of coal, most harmful to health when burned,[7] used almost exclusively as fuel for electric power generation
- Sub-bituminous coal, whose properties range between those of lignite and those of bituminous coal, is used primarily as fuel for steam-electric power generation.
- Bituminous coal, a dense sedimentary rock, usually black, but sometimes dark brown, often with well-defined bands of bright and dull material. It is used primarily as fuel in steam-electric power generation and to make coke. Known as steam coal in the UK, and historically used to raise steam in steam locomotives and ships
- Anthracite coal, the highest rank of coal, is a harder, glossy black coal used primarily for residential and commercial space heating.
- Graphite, a difficult to ignite coal which is mostly used in pencils, or powdered for lubrication.
- Cannel coal (sometimes called "candle coal"), a variety of fine-grained, high-rank coal with significant hydrogen content, which consists primarily of liptinite. It is related to boghead coal.
There are several international standards for coal.[50] The classification of coal is generally based on the content of volatiles. However the most important distinction is between thermal coal (also known as steam coal), which is burnt to generate electricity via steam; and metallurgical coal (also known as coking coal), which is burnt at high temperature to make steel.
Hilt's law is a geological observation that (within a small area) the deeper the coal is found, the higher its rank (or grade). It applies if the thermal gradient is entirely vertical; however, metamorphism may cause lateral changes of rank, irrespective of depth. For example, some of the coal seams of the Madrid, New Mexico coal field were partially converted to anthracite by contact metamorphism from an igneous sill while the remainder of the seams remained as bituminous coal.[51]
History

The earliest recognized use is from the Shenyang area of China where by 4000 BC Neolithic inhabitants had begun carving ornaments from black lignite.[52] Coal from the Fushun mine in northeastern China was used to smelt copper as early as 1000 BC.[53] Marco Polo, the Italian who traveled to China in the 13th century, described coal as "black stones ... which burn like logs", and said coal was so plentiful, people could take three hot baths a week.[54] In Europe, the earliest reference to the use of coal as fuel is from the geological treatise On Stones (Lap. 16) by the Greek scientist Theophrastus (c. 371–287 BC):[55][56]
Among the materials that are dug because they are useful, those known as anthrakes [coals] are made of earth, and, once set on fire, they burn like charcoal [anthrakes]. They are found in Liguria ... and in Elis as one approaches Olympia by the mountain road; and they are used by those who work in metals.
— Theophrastus, On Stones (16) [57]
Outcrop coal was used in Britain during the Bronze Age (3000–2000 BC), where it formed part of funeral pyres.[58][59] In Roman Britain, with the exception of two modern fields, "the Romans were exploiting coals in all the major coalfields in England and Wales by the end of the second century AD".[60] Evidence of trade in coal, dated to about AD 200, has been found at the Roman settlement at Heronbridge, near Chester; and in the Fenlands of East Anglia, where coal from the Midlands was transported via the Car Dyke for use in drying grain.[61] Coal cinders have been found in the hearths of villas and Roman forts, particularly in Northumberland, dated to around AD 400. In the west of England, contemporary writers described the wonder of a permanent brazier of coal on the altar of Minerva at Aquae Sulis (modern day Bath), although in fact easily accessible surface coal from what became the Somerset coalfield was in common use in quite lowly dwellings locally.[62] Evidence of coal's use for iron-working in the city during the Roman period has been found.[63] In Eschweiler, Rhineland, deposits of bituminous coal were used by the Romans for the smelting of iron ore.[60]

No evidence exists of coal being of great importance in Britain before about AD 1000, the High Middle Ages.[64] Coal came to be referred to as "seacoal" in the 13th century; the wharf where the material arrived in London was known as Seacoal Lane, so identified in a charter of King Henry III granted in 1253.[65] Initially, the name was given because much coal was found on the shore, having fallen from the exposed coal seams on cliffs above or washed out of underwater coal outcrops,[64] but by the time of Henry VIII, it was understood to derive from the way it was carried to London by sea.[66] In 1257–1259, coal from Newcastle upon Tyne was shipped to London for the smiths and lime-burners building Westminster Abbey.[64] Seacoal Lane and Newcastle Lane, where coal was unloaded at wharves along the River Fleet, still exist.[67]
These easily accessible sources had largely become exhausted (or could not meet the growing demand) by the 13th century, when underground extraction by shaft mining or adits was developed.[58] The alternative name was "pitcoal", because it came from mines.

Cooking and home heating with coal (in addition to firewood or instead of it) has been done in various times and places throughout human history, especially in times and places where ground-surface coal was available and firewood was scarce, but a widespread reliance on coal for home hearths probably never existed until such a switch in fuels happened in London in the late sixteenth and early seventeenth centuries.[68] Historian Ruth Goodman has traced the socioeconomic effects of that switch and its later spread throughout Britain[68] and suggested that its importance in shaping the industrial adoption of coal has been previously underappreciated.[68]: xiv–xix
The development of the Industrial Revolution led to the large-scale use of coal, as the steam engine took over from the water wheel. In 1700, five-sixths of the world's coal was mined in Britain. Britain would have run out of suitable sites for watermills by the 1830s if coal had not been available as a source of energy.[69] In 1947 there were some 750,000 miners in Britain,[70] but the last deep coal mine in the UK closed in 2015.[71]
A grade between bituminous coal and anthracite was once known as "steam coal" as it was widely used as a fuel for steam locomotives. In this specialized use, it is sometimes known as "sea coal" in the United States.[72] Small "steam coal", also called dry small steam nuts (DSSN), was used as a fuel for domestic water heating.
Coal played an important role in industry in the 19th and 20th century. The predecessor of the European Union, the European Coal and Steel Community, was based on the trading of this commodity.[73]
Coal continues to arrive on beaches around the world from both natural erosion of exposed coal seams and windswept spills from cargo ships. Many homes in such areas gather this coal as a significant, and sometimes primary, source of home heating fuel.[74]
Composition
Coal consists mainly of a black mixture of diverse organic compounds and polymers. Of course, several kinds of coals exist, with variable dark colors and variable compositions. Young coals (brown coal, lignite) are not black. The two main black coals are bituminous, which is more abundant, and anthracite. The % carbon in coal follows the order anthracite > bituminous > lignite > brown coal. The fuel value of coal varies in the same order. Some anthracite deposits contain pure carbon in the form of graphite.
For bituminous coal, the elemental composition on a dry, ash-free basis of 84.4% carbon, 5.4% hydrogen, 6.7% oxygen, 1.7% nitrogen, and 1.8% sulfur, on a weight basis.[40] This composition reflects partly the composition of the precursor plants. The second main fraction of coal is ash, an undesirable, noncombustable mixture of inorganic minerals. The composition of ash is often discussed in terms of oxides obtained after combustion in air:
| SiO2 | 20–40 |
| Al2O3 | 10–35 |
| Fe2O3 | 5–35 |
| CaO | 1–20 |
| MgO | 0.3–4 |
| TiO2 | 0.5–2.5 |
| Na2O & K2O | 1–4 |
| SO3 | 0.1–12[75] |
Of particular interest is the sulfur content of coal, which can vary from less than 1% to as much as 4%. Most of the sulfur and most of the nitrogen is incorporated into the organic fraction in the form of organosulfur compounds and organonitrogen compounds. This sulfur and nitrogen are strongly bound within the hydrocarbon matrix. These elements are released as SO2 and NOx upon combustion. They cannot be removed, economically at least, otherwise. Some coals contain inorganic sulfur, mainly in the form of iron pyrite (FeS2). Being a dense mineral, it can be removed from coal by mechanical means, e.g. by froth flotation. Some sulfate occurs in coal, especially weathered samples. It is not volatilized and can be removed by washing.[46]
Minor components include:
| Substance | Content |
|---|---|
| Mercury (Hg) | 0.10±0.01 ppm[76] |
| Arsenic (As) | 1.4–71 ppm[77] |
| Selenium (Se) | 3 ppm[78] |
As minerals, Hg, As, and Se are not problematic to the environment, especially since they are only trace components. They become however mobile (volatile or water-soluble) when these minerals are combusted.
Uses
Most coal is used as fuel. 27.6% of world energy was supplied by coal in 2017 and Asia used almost three-quarters of it.[79] Other large-scale applications also exist. The energy density of coal is roughly 24 megajoules per kilogram[80] (approximately 6.7 kilowatt-hours per kg). For a coal power plant with a 40% efficiency, it takes an estimated 325 kg (717 lb) of coal to power a 100 W lightbulb for one year.[81]
Electricity generation



In 2022, 68% of global coal use was used for electricity generation.[82]: 11 Coal burnt in coal power stations to generate electricity is called thermal coal. It is usually pulverized and then burned in a furnace with a boiler.[83] The furnace heat converts boiler water to steam, which is then used to spin turbines which turn generators and create electricity.[84] The thermodynamic efficiency of this process varies between about 25% and 50% depending on the pre-combustion treatment, turbine technology (e.g. supercritical steam generator) and the age of the plant.[85][86]
A few integrated gasification combined cycle (IGCC) power plants have been built, which burn coal more efficiently. Instead of pulverizing the coal and burning it directly as fuel in the steam-generating boiler, the coal is gasified to create syngas, which is burned in a gas turbine to produce electricity (just like natural gas is burned in a turbine). Hot exhaust gases from the turbine are used to raise steam in a heat recovery steam generator which powers a supplemental steam turbine. The overall plant efficiency when used to provide combined heat and power can reach as much as 94%.[87] IGCC power plants emit less local pollution than conventional pulverized coal-fueled plants. Other ways to use coal are as coal-water slurry fuel (CWS), which was developed in the Soviet Union, or in an MHD topping cycle. However these are not widely used due to lack of profit.
In 2017 38% of the world's electricity came from coal, the same percentage as 30 years previously.[88] In 2018 global installed capacity was 2TW (of which 1TW is in China) which was 30% of total electricity generation capacity.[89] The most dependent major country is South Africa, with over 80% of its electricity generated by coal;[90] but China alone generates more than half of the world's coal-generated electricity.[91] Efforts around the world to reduce the use of coal have led some regions to switch to natural gas and renewable energy. In 2018 coal-fired power station capacity factor averaged 51%, that is they operated for about half their available operating hours.[92]
Coke

Coke is a solid carbonaceous residue that is used in manufacturing steel and other iron-containing products.[93] Coke is made when metallurgical coal (also known as coking coal) is baked in an oven without oxygen at temperatures as high as 1,000 °C, driving off the volatile constituents and fusing together the fixed carbon and residual ash. Metallurgical coke is used as a fuel and as a reducing agent in smelting iron ore in a blast furnace.[94] The carbon monoxide produced by its combustion reduces hematite (an iron oxide) to iron.
- 2 Fe2O3 + 6 CO → 4 Fe + 6 CO2
Pig iron, which is too rich in dissolved carbon, is also produced.
The coke must be strong enough to resist the weight of overburden in the blast furnace, which is why coking coal is so important in making steel using the conventional route. Coke from coal is grey, hard, and porous and has a heating value of 29.6 MJ/kg. Some coke-making processes produce byproducts, including coal tar, ammonia, light oils, and coal gas.
Petroleum coke (petcoke) is the solid residue obtained in oil refining, which resembles coke but contains too many impurities to be useful in metallurgical applications.
Production of chemicals

Chemicals have been produced from coal since the 1950s. Coal can be used as a feedstock in the production of a wide range of chemical fertilizers and other chemical products. The main route to these products was coal gasification to produce syngas. Primary chemicals that are produced directly from the syngas include methanol, hydrogen, and carbon monoxide, which are the chemical building blocks from which a whole spectrum of derivative chemicals are manufactured, including olefins, acetic acid, formaldehyde, ammonia, urea, and others. The versatility of syngas as a precursor to primary chemicals and high-value derivative products provides the option of using coal to produce a wide range of commodities. In the 21st century, however, the use of coal bed methane is becoming more important.[95]
Because the slate of chemical products that can be made via coal gasification can in general also use feedstocks derived from natural gas and petroleum, the chemical industry tends to use whatever feedstocks are most cost-effective. Therefore, interest in using coal tended to increase for higher oil and natural gas prices and during periods of high global economic growth that might have strained oil and gas production.
Coal to chemical processes require substantial quantities of water.[96] Much coal to chemical production is in China[97][98] where coal dependent provinces such as Shanxi are struggling to control its pollution.[99]
Liquefaction
Coal can be converted directly into synthetic fuels equivalent to gasoline or diesel by hydrogenation or carbonization.[100] Coal liquefaction emits more carbon dioxide than liquid fuel production from crude oil. Mixing in biomass and using carbon capture and storage (CCS) would emit slightly less than the oil process but at a high cost.[101] State owned China Energy Investment runs a coal liquefaction plant and plans to build 2 more.[102]
Coal liquefaction may also refer to the cargo hazard when shipping coal.[103]
Gasification
Coal gasification, as part of an integrated gasification combined cycle (IGCC) coal-fired power station, is used to produce syngas, a mixture of carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H2) gas to fire gas turbines to produce electricity. Syngas can also be converted into transportation fuels, such as gasoline and diesel, through the Fischer–Tropsch process; alternatively, syngas can be converted into methanol, which can be blended into fuel directly or converted to gasoline via the methanol to gasoline process.[104] Gasification combined with Fischer–Tropsch technology was used by the Sasol chemical company of South Africa to make chemicals and motor vehicle fuels from coal.[105]
During gasification, the coal is mixed with oxygen and steam while also being heated and pressurized. During the reaction, oxygen and water molecules oxidize the coal into carbon monoxide (CO), while also releasing hydrogen gas (H2). This used to be done in underground coal mines, and also to make town gas, which was piped to customers to burn for illumination, heating, and cooking.
- 3C (as Coal) + O2 + H2O → H2 + 3CO
If the refiner wants to produce gasoline, the syngas is routed into a Fischer–Tropsch reaction. This is known as indirect coal liquefaction. If hydrogen is the desired end-product, however, the syngas is fed into the water gas shift reaction, where more hydrogen is liberated:
- CO + H2O → CO2 + H2
Coal industry
Mining

About 8,000 Mt of coal are produced annually, about 90% of which is hard coal and 10% lignite. As of 2018[update] just over half is from underground mines.[106] The coal mining industry employs almost 2.7 million workers.[107] More accidents occur during underground mining than surface mining. Not all countries publish mining accident statistics so worldwide figures are uncertain, but it is thought that most deaths occur in coal mining accidents in China: in 2017 there were 375 coal mining related deaths in China.[108] Most coal mined is thermal coal (also called steam coal as it is used to make steam to generate electricity) but metallurgical coal (also called "metcoal" or "coking coal" as it is used to make coke to make iron) accounts for 10% to 15% of global coal use.[109]
As a traded commodity

China mines almost half the world's coal, followed by India with about a tenth.[110] At 471 Mt and a 34% share of global exports, Indonesia was the largest exporter by volume in 2022, followed by Australia with 344 Mt and Russia with 224 Mt.[111] Other major exporters of coal are the United States, South Africa, Colombia, and Canada.[82]: 118 In 2022, China, India, and Japan were the biggest importers of coal, importing 301, 228, and 184 Mt respectively.[82]: 117 Russia is increasingly orienting its coal exports from Europe to Asia as Europe transitions to renewable energy and subjects Russia to sanctions over its invasion of Ukraine.[18]
The price of metallurgical coal is volatile[112] and much higher than the price of thermal coal because metallurgical coal must be lower in sulfur and requires more cleaning.[113] Coal futures contracts provide coal producers and the electric power industry an important tool for hedging and risk management.
In some countries, new onshore wind or solar generation already costs less than coal power from existing plants.[114][115] However, for China this is forecast for the early 2020s[116] and for southeast Asia not until the late 2020s.[117] In India, building new plants is uneconomic and, despite being subsidized, existing plants are losing market share to renewables.[118]
In many countries in the Global North, there is a move away from the use of coal and former mine sites are being used as a tourist attraction.[119]
Market trends

In 2022, China used 4520 Mt of coal, comprising more than half of global coal consumption. India, the European Union, and the United States, were the next largest consumers of coal, using 1162, 461, and 455 Mt respectively.[82]: 114 Over the past decade, China has almost always accounted for the lion's share of the global growth in coal demand.[120] Therefore, international market trends depend on Chinese energy policy.[121]
Although the government effort to reduce air pollution in China means that the global long-term trend is to burn less coal, the short and medium term trends may differ, in part due to Chinese financing of new coal-fired power plants in other countries.[89]
Preliminary analysis by International Energy Agency (IEA) indicates that global coal exports reached an all-time high in 2023. Through to 2026, the IEA expects global coal trade to decline by about 12%, driven by growing domestic production in coal-intensive economies such as China and India and coal phase-out plans elsewhere, such as in Europe.[111] While thermal coal exports are expected to decline by about 16% by 2026, exports of metallurgical coal are expected to slightly increase by almost 2%.[111]
Damage to human health
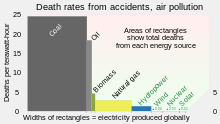
The use of coal as fuel causes health problems and deaths.[123] The mining and processing of coal causes air and water pollution.[124] Coal-powered plants emit nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, particulate pollution, and heavy metals, which adversely affect human health.[124] Coal bed methane extraction is important to avoid mining accidents.
The deadly London smog was caused primarily by the heavy use of coal. Globally coal is estimated to cause 800,000 premature deaths every year,[125] mostly in India[126] and China.[127][128][129]
Burning coal is a major contributor to sulfur dioxide emissions, which creates PM2.5 particulates, the most dangerous form of air pollution.[130]
Coal smokestack emissions cause asthma, strokes, reduced intelligence, artery blockages, heart attacks, congestive heart failure, cardiac arrhythmias, mercury poisoning, arterial occlusion, and lung cancer.[131][132]
Annual health costs in Europe from use of coal to generate electricity are estimated at up to €43 billion.[133]
In China, early deaths due to air pollution coal plants have been estimated at 200 per GW-year, however they may be higher around power plants where scrubbers are not used or lower if they are far from cities.[134] Improvements to China's air quality and human health would grow with more stringent climate policies, mainly because the country's energy is so heavily reliant on coal. And there would be a net economic benefit.[135]
A 2017 study in the Economic Journal found that for Britain during the period 1851–1860, "a one standard deviation increase in coal use raised infant mortality by 6–8% and that industrial coal use explains roughly one-third of the urban mortality penalty observed during this period."[136]
Breathing in coal dust causes coalworker's pneumoconiosis or "black lung", so called because the coal dust literally turns the lungs black.[137] In the US alone, it is estimated that 1,500 former employees of the coal industry die every year from the effects of breathing in coal mine dust.[138]
Huge amounts of coal ash and other waste is produced annually. Use of coal generates hundreds of millions of tons of ash and other waste products every year. These include fly ash, bottom ash, and flue-gas desulfurization sludge, that contain mercury, uranium, thorium, arsenic, and other heavy metals, along with non-metals such as selenium.[139]
Around 10% of coal is ash.[140] Coal ash is hazardous and toxic to human beings and some other living things.[141] Coal ash contains the radioactive elements uranium and thorium. Coal ash and other solid combustion byproducts are stored locally and escape in various ways that expose those living near coal plants to radiation and environmental toxics.[142]
Damage to the environment

Coal mining, coal combustion wastes, and flue gas are causing major environmental damage.[143][144]
Water systems are affected by coal mining.[145] For example, the mining of coal affects groundwater and water table levels and acidity. Spills of fly ash, such as the Kingston Fossil Plant coal fly ash slurry spill, can also contaminate land and waterways, and destroy homes. Power stations that burn coal also consume large quantities of water. This can affect the flows of rivers, and has consequential impacts on other land uses. In areas of water scarcity, such as the Thar Desert in Pakistan, coal mining and coal power plants contribute to the depletion of water resources.[146]
One of the earliest known impacts of coal on the water cycle was acid rain. In 2014, approximately 100 Tg/S of sulfur dioxide (SO2) was released, over half of which was from burning coal.[147] After release, the sulfur dioxide is oxidized to H2SO4 which scatters solar radiation, hence its increase in the atmosphere exerts a cooling effect on the climate. This beneficially masks some of the warming caused by increased greenhouse gases. However, the sulfur is precipitated out of the atmosphere as acid rain in a matter of weeks,[148] whereas carbon dioxide remains in the atmosphere for hundreds of years. Release of SO2 also contributes to the widespread acidification of ecosystems.[149]
Disused coal mines can also cause issues. Subsidence can occur above tunnels, causing damage to infrastructure or cropland. Coal mining can also cause long lasting fires, and it has been estimated that thousands of coal seam fires are burning at any given time.[150] For example, Brennender Berg has been burning since 1668, and is still burning in the 21st century.[151]
The production of coke from coal produces ammonia, coal tar, and gaseous compounds as byproducts which if discharged to land, air or waterways can pollute the environment.[152] The Whyalla steelworks is one example of a coke producing facility where liquid ammonia was discharged to the marine environment.[153]
Climate change

The largest and most long-term effect of coal use is the release of carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas that causes climate change. Coal-fired power plants were the single largest contributor to the growth in global CO2 emissions in 2018,[155] 40% of the total fossil fuel emissions,[9] and more than a quarter of total emissions.[8][note 1] Coal mining can emit methane, another greenhouse gas.[156][157]
In 2016 world gross carbon dioxide emissions from coal usage were 14.5 gigatonnes.[158] For every megawatt-hour generated, coal-fired electric power generation emits around a tonne of carbon dioxide, which is double the approximately 500 kg of carbon dioxide released by a natural gas-fired electric plant.[159] The emission intensity of coal varies with type and generator technology and exceeds 1200 g per kWh in some countries.[160] In 2013, the head of the UN climate agency advised that most of the world's coal reserves should be left in the ground to avoid catastrophic global warming.[161] To keep global warming below 1.5 °C or 2 °C hundreds, or possibly thousands, of coal-fired power plants will need to be retired early.[162]
Underground fires
Thousands of coal fires are burning around the world.[163] Those burning underground can be difficult to locate and many cannot be extinguished. Fires can cause the ground above to subside, their combustion gases are dangerous to life, and breaking out to the surface can initiate surface wildfires. Coal seams can be set on fire by spontaneous combustion or contact with a mine fire or surface fire. Lightning strikes are an important source of ignition. The coal continues to burn slowly back into the seam until oxygen (air) can no longer reach the flame front. A grass fire in a coal area can set dozens of coal seams on fire.[164][165] Coal fires in China burn an estimated 120 million tons of coal a year, emitting 360 million metric tons of CO2, amounting to 2–3% of the annual worldwide production of CO2 from fossil fuels.[166][167]
Pollution mitigation and carbon capture

Systems and technologies exist to mitigate the health and environmental impact of burning coal for energy.
Precombustion treatment
Refined coal is the product of a coal-upgrading technology that removes moisture and certain pollutants from lower-rank coals such as sub-bituminous and lignite (brown) coals. It is one form of several precombustion treatments and processes for coal that alter coal's characteristics before it is burned. Thermal efficiency improvements are achievable by improved pre-drying (especially relevant with high-moisture fuel such as lignite or biomass).[168] The goals of precombustion coal technologies are to increase efficiency and reduce emissions when the coal is burned. Precombustion technology can sometimes be used as a supplement to postcombustion technologies to control emissions from coal-fueled boilers.
Post combustion approaches
Post combustion approaches to mitigate pollution include flue-gas desulfurization, selective catalytic reduction, electrostatic precipitators, and fly ash reduction.
Carbon capture and storage
Carbon capture and storage (CCS) can be used to capture carbon dioxide from the flue gas of coal power plants and bury it securely in an underground reservoir. Between 1972 and 2017, plans were made to add CCS to enough coal and gas power plants to sequester 161 million tonnes of CO
2 per year, but by 2021 98% of these plans had failed.[169] Cost, the absence of measures to address long-term liability for stored CO2, and limited social acceptability have all contributed to project cancellations.[170]: 133 As of 2024, CCS is in operation at only four coal power plants and one gas power plant worldwide.[171]
"Clean coal" and "abated coal"

Since the mid-1980s, the term "clean coal" has been widely used with various meanings.[173] Initially, "clean coal technology" referred to scrubbers and catalytic converters that reduced the pollutants that cause acid rain. The scope then expanded to include reduction of other pollutants such as mercury.[173] Recently, the term has come to encompass the use of CCS to reduce greenhouse gas emissions (GHG).[173] In political discourse, the phrase "clean coal" is sometimes used to suggest that coal itself can be clean.[173] This suggestion is false: Technologies to mitigate emissions are implemented in the plants where coal is processed and burned, but coal as a product is intrinsically dirty.[173]
In discussions on greenhouse gas emissions, another common term is "abatement" of coal use. In the 2023 United Nations Climate Change Conference, an agreement was reached to phase down unabated coal use.[174] Since the term abated was not defined, the agreement was criticized for being open to abuse.[174] Without a clear definition, is possible for fossil fuel use to be called "abated" if it uses CCS only in a minimal fashion, such as capturing only 30% of the emissions from a plant.[174]
The IPCC considers fossil fuels to be unabated if they are "produced and used without interventions that substantially reduce the amount of GHG emitted throughout the life-cycle; for example, capturing 90% or more from power plants."[175][176]
Economics
In 2018 US$80 billion was invested in coal supply but almost all for sustaining production levels rather than opening new mines.[177] In the long term coal and oil could cost the world trillions of dollars per year.[178][179] Coal alone may cost Australia billions,[180] whereas costs to some smaller companies or cities could be on the scale of millions of dollars.[181] The economies most damaged by coal (via climate change) may be India and the US as they are the countries with the highest social cost of carbon.[182] Bank loans to finance coal are a risk to the Indian economy.[126]
China is the largest producer of coal in the world. It is the world's largest energy consumer, and coal in China supplies 60% of its primary energy. However two fifths of China's coal power stations are estimated to be loss-making.[116]
Air pollution from coal storage and handling costs the US almost 200 dollars for every extra ton stored, due to PM2.5.[183] Coal pollution costs the €43 billion each year.[184] Measures to cut air pollution benefit individuals financially and the economies of countries[185][186] such as China.[187]
Subsidies
Subsidies for coal in 2021 have been estimated at US$19 billion, not including electricity subsidies, and are expected to rise in 2022.[188] As of 2019[update] G20 countries provide at least US$63.9 billion[155] of government support per year for the production of coal, including coal-fired power: many subsidies are impossible to quantify[189] but they include US$27.6 billion in domestic and international public finance, US$15.4 billion in fiscal support, and US$20.9 billion in state-owned enterprise (SOE) investments per year.[155] In the EU state aid to new coal-fired plants is banned from 2020, and to existing coal-fired plants from 2025.[190] As of 2018, government funding for new coal power plants was supplied by Exim Bank of China,[191] the Japan Bank for International Cooperation and Indian public sector banks.[192] Coal in Kazakhstan was the main recipient of coal consumption subsidies totalling US$2 billion in 2017.[193] Coal in Turkey benefited from substantial subsidies in 2021.[194]
Stranded assets
Some coal-fired power stations could become stranded assets, for example China Energy Investment, the world's largest power company, risks losing half its capital.[116] However, state-owned electricity utilities such as Eskom in South Africa, Perusahaan Listrik Negara in Indonesia, Sarawak Energy in Malaysia, Taipower in Taiwan, EGAT in Thailand, Vietnam Electricity and EÜAŞ in Turkey are building or planning new plants.[195] As of 2021 this may be helping to cause a carbon bubble which could cause financial instability if it bursts.[196][197][198]
Politics
Countries building or financing new coal-fired power stations, such as China, India, Indonesia, Vietnam, Turkey and Bangladesh, face mounting international criticism for obstructing the aims of the Paris Agreement.[89][199][200] In 2019, the Pacific Island nations (in particular Vanuatu and Fiji) criticized Australia for failing to cut their emissions at a faster rate than they were, citing concerns about coastal inundation and erosion.[201] In May 2021, the G7 members agreed to end new direct government support for international coal power generation.[202]

Cultural usage
Coal is the official state mineral of Kentucky,[203] and the official state rock of Utah[204] and West Virginia.[205] These US states have a historic link to coal mining.
Some cultures hold that children who misbehave will receive only a lump of coal from Santa Claus for Christmas in their stockings instead of presents.
It is also customary and considered lucky in Scotland to give coal as a gift on New Year's Day. This occurs as part of first-footing and represents warmth for the year to come.[206]
See also
- Biochar – Lightweight black residue, made of carbon and ashes, after pyrolysis of biomass
- Carbochemistry – Branch of chemistry
- Coal analysis – Measurement of properties of coal
- Coal blending – Mixing of mined coal
- Coal homogenization – Process of mixing coal to reduce variance
- Coal measures (stratigraphic unit)
- Health and environmental impact of the coal industry
- Fluidized bed combustion – Technology used to burn solid fuels
- Fossil fuel phase-out – Gradual reduction of the use and production of fossil fuels
- Gytta – type of fine grained sedimentary mud
- Coal-mining region – Basin with coal deposits
- Mountaintop removal mining – Type of surface mining
- Subcoal – Coal substitute made from recycled waste
- The Coal Question – Book by William Stanley Jevons
- Tonstein – Type of sedimentary rock
- FutureCoal – international non-profit, non-governmental association based in London representing the global coal industry
- Épinac coal mine
Notes
- ^ 14.4 gigatonnes coal/50 gigatonnes total
References
- ^ Blander, M. "Calculations of the Influence of Additives on Coal Combustion Deposits" (PDF). Argonne National Laboratory. p. 315. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 May 2010. Retrieved 17 December 2011.
- ^ a b "Coal Explained". Energy Explained. US Energy Information Administration. 21 April 2017. Archived from the original on 8 December 2017. Retrieved 13 November 2017.
- ^ Cleal, C. J.; Thomas, B. A. (2005). "Palaeozoic tropical rainforests and their effect on global climates: is the past the key to the present?". Geobiology. 3 (1): 13–31. Bibcode:2005Gbio....3...13C. doi:10.1111/j.1472-4669.2005.00043.x. ISSN 1472-4669. S2CID 129219852.
- ^ Sahney, S.; Benton, M.J.; Falcon-Lang, H.J. (2010). "Rainforest collapse triggered Pennsylvanian tetrapod diversification in Euramerica". Geology. 38 (12): 1079–1082. Bibcode:2010Geo....38.1079S. doi:10.1130/G31182.1.
- ^ Wilde, Robert (30 June 2019). "How the Demand for Coal Impacted the Industrial Revolution". ThoughtCo. Retrieved 2 May 2024.
- ^ "Global energy data". International Energy Agency.
- ^ a b "Lignite coal – health effects and recommendations from the health sector" (PDF). Health and Environment Alliance. December 2018. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 December 2018. Retrieved 12 February 2024.
- ^ a b Ritchie, Hannah; Roser, Max (11 May 2020). "CO2 emissions by fuel". Our World in Data. Retrieved 22 January 2021.
- ^ a b "China's unbridled export of coal power imperils climate goals". Retrieved 7 December 2018.
- ^ "Dethroning King Coal – How a Once Dominant Fuel Source is Falling Rapidly from Favour". Resilience. 24 January 2020. Retrieved 8 February 2020.
- ^ "Analysis: The global coal fleet shrank for first time on record in 2020". Carbon Brief. 3 August 2020. Retrieved 9 November 2021.
- ^ Simon, Frédéric (21 April 2020). "Sweden adds name to growing list of coal-free states in Europe". www.euractiv.com. Retrieved 9 November 2021.
- ^ "Tax carbon, not people: UN chief issues climate plea from Pacific 'frontline'". The Guardian. 15 May 2019.
- ^ Anmar Frangoul (27 July 2023). "IEA says coal use hit an all-time high last year — and global demand will persist near record levels". CNBC. Retrieved 10 September 2023.
- ^ Frangoul, Frangoul (27 July 2023). "Global coal demand set to remain at record levels in 2023". iea. Retrieved 12 September 2023.
- ^ "Analysis: Why coal use must plummet this decade to keep global warming below 1.5C". Carbon Brief. 6 February 2020. Retrieved 8 February 2020.
- ^ "Exports – Coal Information: Overview – Analysis". IEA. Retrieved 20 January 2022.
- ^ a b Overland, Indra; Loginova, Julia (1 August 2023). "The Russian coal industry in an uncertain world: Finally pivoting to Asia?". Energy Research & Social Science. 102: 103150. Bibcode:2023ERSS..10203150O. doi:10.1016/j.erss.2023.103150. ISSN 2214-6296.
- ^ a b Harper, Douglas. "coal". Online Etymology Dictionary.
- ^ "How Coal Is Formed". Archived from the original on 18 January 2017.
- ^ "Coal". British Geological Survey. March 2010.
- ^ Taylor, Thomas N; Taylor, Edith L; Krings, Michael (2009). Paleobotany: The Biology and Evolution of Fossil Plants. Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-12-373972-8. Archived from the original on 16 May 2016.
- ^ "Heat, time, pressure, and coalification". Kentucky Geological Survey. University of Kentucky. Retrieved 28 November 2020.
- ^ "Burial temperatures from coal". Kentucky Geological Survey. University of Kentucky. Retrieved 28 November 2020.
- ^ McGhee, George R. (2018). Carboniferous Giants and Mass Extinction: The Late Paleozoic Ice Age World. New York: Columbia University Press. p. 98. ISBN 9780231180979.
- ^ McGhee 2018, pp. 88–92.
- ^ Retallack, G. J.; Veevers, J. J.; Morante, R. (1996). "Global coal gap between Permian–Triassic extinctions and middle Triassic recovery of peat forming plants". GSA Bulletin. 108 (2): 195–207. Bibcode:1996GSAB..108..195R. doi:10.1130/0016-7606(1996)108<0195:GCGBPT>2.3.CO;2.
- ^ McGhee 2018, p. 99.
- ^ McGhee 2018, pp. 98–102.
- ^ Koonin, Steven E. (2021). Unsettled: What Climate Science Tells Us, What It Doesn't, and Why It Matters. Dallas: BenBella Books. p. 44. ISBN 9781953295248.
- ^ Floudas, Dimitrios; Binder, Manfred; Riley, Robert; Barry, Kerrie; Blanchette, Robert A.; Henrissat, Bernard; Martínez, Angel T.; Otillar, Robert; Spatafora, Joseph W.; Yadav, Jagjit S.; Aerts, Andrea; Benoit, Isabelle; Boyd, Alex; Carlson, Alexis; Copeland, Alex; Coutinho, Pedro M.; de Vries, Ronald P.; Ferreira, Patricia; Findley, Keisha; Foster, Brian; Gaskell, Jill; Glotzer, Dylan; Górecki, Paweł; Heitman, Joseph; Hesse, Cedar; Hori, Chiaki; Igarashi, Kiyohiko; Jurgens, Joel A.; Kallen, Nathan; Kersten, Phil; Kohler, Annegret; Kües, Ursula; Kumar, T. K. Arun; Kuo, Alan; LaButti, Kurt; Larrondo, Luis F.; Lindquist, Erika; Ling, Albee; Lombard, Vincent; Lucas, Susan; Lundell, Taina; Martin, Rachael; McLaughlin, David J.; Morgenstern, Ingo; Morin, Emanuelle; Murat, Claude; Nagy, Laszlo G.; Nolan, Matt; Ohm, Robin A.; Patyshakuliyeva, Aleksandrina; Rokas, Antonis; Ruiz-Dueñas, Francisco J.; Sabat, Grzegorz; Salamov, Asaf; Samejima, Masahiro; Schmutz, Jeremy; Slot, Jason C.; St. John, Franz; Stenlid, Jan; Sun, Hui; Sun, Sheng; Syed, Khajamohiddin; Tsang, Adrian; Wiebenga, Ad; Young, Darcy; Pisabarro, Antonio; Eastwood, Daniel C.; Martin, Francis; Cullen, Dan; Grigoriev, Igor V.; Hibbett, David S. (29 June 2012). "The Paleozoic Origin of Enzymatic Lignin Decomposition Reconstructed from 31 Fungal Genomes". Science. 336 (6089): 1715–1719. Bibcode:2012Sci...336.1715F. doi:10.1126/science.1221748. hdl:10261/60626. OSTI 1165864. PMID 22745431. S2CID 37121590.
- ^ "White Rot Fungi Slowed Coal Formation". Scientific American.
- ^ Nelsen, Matthew P.; DiMichele, William A.; Peters, Shanan E.; Boyce, C. Kevin (19 January 2016). "Delayed fungal evolution did not cause the Paleozoic peak in coal production". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 113 (9): 2442–2447. Bibcode:2016PNAS..113.2442N. doi:10.1073/pnas.1517943113. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 4780611. PMID 26787881.
- ^ Ayuso-Fernandez I, Ruiz-Duenas FJ, Martinez AT: Evolutionary convergence in lignin-degrading enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2018, 115:6428-6433.
- ^ Otto-Bliesner, Bette L. (15 September 1993). "Tropical mountains and coal formation: A climate model study of the Westphalian (306 MA)". Geophysical Research Letters. 20 (18): 1947–1950. Bibcode:1993GeoRL..20.1947O. doi:10.1029/93GL02235.
- ^ Tyler, S.A.; Barghoorn, E.S.; Barrett, L.P. (1957). "Anthracitic Coal from Precambrian Upper Huronian Black Shale of the Iron River District, Northern Michigan". Geological Society of America Bulletin. 68 (10): 1293. Bibcode:1957GSAB...68.1293T. doi:10.1130/0016-7606(1957)68[1293:ACFPUH]2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0016-7606.
- ^ Mancuso, J.J.; Seavoy, R.E. (1981). "Precambrian coal or anthraxolite; a source for graphite in high-grade schists and gneisses". Economic Geology. 76 (4): 951–54. Bibcode:1981EcGeo..76..951M. doi:10.2113/gsecongeo.76.4.951.
- ^ Stanley, Steven M. Earth System History. New York: W.H. Freeman and Company, 1999. ISBN 0-7167-2882-6 (p. 426)
- ^ Andriesse, J. P. (1988). "The Main Characteristics of Tropical Peats". Nature and Management of Tropical Peat Soils. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. ISBN 92-5-102657-2.
- ^ a b Reid, William (1973). "Chapter 9: Heat Generation, Transport, and Storage". In Robert Perry; Cecil Chilton (eds.). Chemical Engineers' Handbook (5 ed.).
- ^ Ulbrich, Markus; Preßl, Dieter; Fendt, Sebastian; Gaderer, Matthias; Spliethoff, Hartmut (December 2017). "Impact of HTC reaction conditions on the hydrochar properties and CO2 gasification properties of spent grains". Fuel Processing Technology. 167: 663–669. doi:10.1016/j.fuproc.2017.08.010.
- ^ a b Hatcher, Patrick G.; Faulon, Jean Loup; Wenzel, Kurt A.; Cody, George D. (November 1992). "A structural model for lignin-derived vitrinite from high-volatile bituminous coal (coalified wood)". Energy & Fuels. 6 (6): 813–820. doi:10.1021/ef00036a018.
- ^ "Coal Types, Formation and Methods of Mining". Eastern Pennsylvania Coalition for Abandoned Mine Reclamation. Retrieved 29 November 2020.
- ^ Ibarra, JoséV.; Muñoz, Edgar; Moliner, Rafael (June 1996). "FTIR study of the evolution of coal structure during the coalification process". Organic Geochemistry. 24 (6–7): 725–735. Bibcode:1996OrGeo..24..725I. doi:10.1016/0146-6380(96)00063-0.
- ^ Li, Yong; Zhang, Cheng; Tang, Dazhen; Gan, Quan; Niu, Xinlei; Wang, Kai; Shen, Ruiyang (October 2017). "Coal pore size distributions controlled by the coalification process: An experimental study of coals from the Junggar, Ordos and Qinshui basins in China". Fuel. 206: 352–363. Bibcode:2017Fuel..206..352L. doi:10.1016/j.fuel.2017.06.028.
- ^ a b Hower, James (2016). "Coal". Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. pp. 1–63. doi:10.1002/0471238961.0315011222151818.a01.pub3. ISBN 978-0-471-48494-3.
- ^ "Sub-Bituminous Coal". Kentucky Geological Survey. University of Kentucky. Retrieved 29 November 2020.
- ^ "Bituminous Coal". Kentucky Geological Survey. University of Kentucky. Retrieved 29 November 2020.
- ^ "Anthracitic Coal". Kentucky Geological Survey. University of Kentucky. Retrieved 29 November 2020.
- ^ "Standards catalogue 73.040 – Coals". ISO.
- ^ Darton, Horatio Nelson (1916). "Guidebook of the Western United States: Part C - The Santa Fe Route, with a side trip to Grand Canyon of the Colorado". U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin. 613: 81. Bibcode:1916usgs.rept....2D. doi:10.3133/b613. hdl:2027/hvd.32044055492656.
- ^ Golas, Peter J and Needham, Joseph (1999) Science and Civilisation in China. Cambridge University Press. pp. 186–91. ISBN 0-521-58000-5
- ^ coal Archived 2 May 2015 at the Wayback Machine. Encyclopædia Britannica.
- ^ Marco Polo In China. Facts and Details. Retrieved on 11 May 2013. Archived 21 September 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Carol, Mattusch (2008). Oleson, John Peter (ed.). Metalworking and Tools. The Oxford Handbook of Engineering and Technology in the Classical World. Oxford University Press. pp. 418–38 (432). ISBN 978-0-19-518731-1.
- ^ Irby-Massie, Georgia L.; Keyser, Paul T. (2002). Greek Science of the Hellenistic Era: A Sourcebook. Routledge. 9.1 "Theophrastos", p. 228. ISBN 978-0-415-23847-2. Archived from the original on 5 February 2016.
- ^ "το δ' εκ της κατακαύσεως ὅμοιον γίνεται γη κεκαυμένη. οὓς δε καλοῦσιν ευθὺς ἄνθρακας των ὀρυττομένων δια την χρείαν εισί γεώδεις, ἐκκαίονται δε και πυροῦνται καθάπερ οἱ ἄνθρακες. εισὶ δε περί τε την Λιγυστικὴν ὅπου και το ἤλεκτρον, και εν τη Ήλεία βαδιζόντων Όλυμπίαζε την δι' ὄρους, οΐς και οἱ χαλκεΐς χρῶνται." ΠΕΡΙ ΛΙΘΩΝ, p. 21.
- ^ a b Britannica 2004: Coal mining: ancient use of outcropping coal
- ^ Needham, Joseph; Golas, Peter J (1999). Science and Civilisation in China. Cambridge University Press. pp. 186–91. ISBN 978-0-521-58000-7.
- ^ a b Smith, A.H.V. (1997). "Provenance of Coals from Roman Sites in England and Wales". Britannia. 28: 297–324 (322–24). doi:10.2307/526770. JSTOR 526770. S2CID 164153278.
- ^ Salway, Peter (2001). A History of Roman Britain. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-280138-8.
- ^ Forbes, RJ (1966): Studies in Ancient Technology. Brill Academic Publishers, Boston.
- ^ Cunliffe, Barry W. (1984). Roman Bath Discovered. London: Routledge. pp. 14–15, 194. ISBN 978-0-7102-0196-6.
- ^ a b c Cantril, T.C. (1914). Coal Mining. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 3–10. OCLC 156716838.
- ^ "coal, 5a". Oxford English Dictionary. Oxford University Press. 1 December 2010.
- ^ John Caius, quoted in Cantril (1914).
- ^ Trench, Richard; Hillman, Ellis (1993). London Under London: A Subterranean Guide (Second ed.). London: John Murray. p. 33. ISBN 978-0-7195-5288-5.
- ^ a b c Goodman, Ruth (2020), The Domestic Revolution: How the Introduction of Coal Into Victorian Homes Changed Everything, Liveright, ISBN 978-1631497636.
- ^ Wrigley, EA (1990). Continuity, Chance and Change: The Character of the Industrial Revolution in England. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-39657-8.
- ^ "The fall of King Coal". BBC News. 6 December 1999. Archived from the original on 6 March 2016.
- ^ "UK's last deep coal mine Kellingley Colliery capped off". BBC. 14 March 2016.
- ^ Funk and Wagnalls, quoted in "sea-coal". Oxford English Dictionary (2 ed.). Oxford University Press. 1989.
- ^ "The European Coal and Steel Community". EU Learning. Carleton University School of European Studies. Archived from the original on 17 April 2015. Retrieved 14 August 2021.
- ^ Bolton, Aaron; Homer, KBBI- (22 March 2018). "Cost of Cold: Staying warm in Homer". Alaska Public Media. Retrieved 25 January 2019.
- ^ Combines with other oxides to make sulfates.
- ^ Ya. E. Yudovich, M.P. Ketris (21 April 2010). "Mercury in coal: a review; Part 1. Geochemistry" (PDF). labtechgroup.com. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 September 2014. Retrieved 22 February 2013.
- ^ "Arsenic in Coal" (PDF). pubs.usgs.gov. 28 March 2006. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 May 2013. Retrieved 22 February 2013.
- ^ Lakin, Hubert W. (1973). "Selenium in Our Enviroment [sic]". Selenium in Our Environment – Trace Elements in the Environment. Advances in Chemistry. Vol. 123. p. 96. doi:10.1021/ba-1973-0123.ch006. ISBN 978-0-8412-0185-9.
- ^ "Primary energy". BP. Retrieved 5 December 2018.
- ^ Fisher, Juliya (2003). "Energy Density of Coal". The Physics Factbook. Archived from the original on 7 November 2006. Retrieved 25 August 2006.
- ^ "How much coal is required to run a 100-watt light bulb 24 hours a day for a year?". Howstuffworks. 3 October 2000. Archived from the original on 7 August 2006. Retrieved 25 August 2006.
- ^ a b c d "Coal 2023 – Analysis". IEA. 15 December 2023. Retrieved 28 October 2024.
- ^ Total World Electricity Generation by Fuel (2006) Archived 22 October 2015 at the Wayback Machine. Source: IEA 2008.
- ^ "Fossil Power Generation". Siemens AG. Archived from the original on 29 September 2009. Retrieved 23 April 2009.
- ^ J. Nunn, A. Cottrell, A. Urfer, L. Wibberley and P. Scaife, "A Lifecycle Assessment of the Victorian Energy Grid" Archived 2 September 2016 at the Wayback Machine, Cooperative Research Centre for Coal in Sustainable Development, February 2003, p. 7.
- ^ "Neurath F and G set new benchmarks" (PDF). Alstom. Archived (PDF) from the original on 1 April 2015. Retrieved 21 July 2014.
- ^ Avedøreværket Archived 29 January 2016 at the Wayback Machine. Ipaper.ipapercms.dk. Retrieved on 11 May 2013.
- ^ "The most depressing energy chart of the year". Vox. 15 June 2018. Retrieved 30 October 2018.
- ^ a b c Cornot-Gandolfe, Sylvie (May 2018). A Review of Coal Market Trends and Policies in 2017 (PDF). Ifri. Archived (PDF) from the original on 15 November 2018.
- ^ "Energy Revolution: A Global Outlook" (PDF). Drax. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 February 2019. Retrieved 7 February 2019.
- ^ "China generated over half world's coal-fired power in 2020: study". Reuters. 28 March 2021. Retrieved 14 September 2021.
China generated 53% of the world's total coal-fired power in 2020, nine percentage points more that five years earlier
- ^ Shearer, Christine; Myllyvirta, Lauri; Yu, Aiqun; Aitken, Greig; Mathew-Shah, Neha; Dallos, Gyorgy; Nace, Ted (March 2020). Boom and Bust 2020: Tracking the Global Coal Plant Pipeline (PDF) (Report). Global Energy Monitor. Archived from the original on 27 March 2020. Retrieved 27 April 2020.
- ^ "How is Steel Produced?". World Coal Association. 28 April 2015. Archived from the original on 12 April 2017. Retrieved 8 April 2017.
- ^ Blast furnace steelmaking cost model Archived 14 January 2016 at the Wayback Machine. Steelonthenet.com. Retrieved on 24 August 2012.
- ^ "Coal India begins process of developing Rs 2,474 crore CBM projects | Hellenic Shipping News Worldwide". www.hellenicshippingnews.com. Retrieved 31 May 2020.
- ^ "Coal-to-Chemicals: Shenhua's Water Grab". China Water Risk. Retrieved 31 May 2020.
- ^ Rembrandt (2 August 2012). "China's Coal to Chemical Future" (Blog post by expert). The Oil Drum.Com. Retrieved 3 March 2013.
- ^ Yin, Ken (27 February 2012). "China develops coal-to-olefins projects, which could lead to ethylene self-sufficiency". ICIS Chemical Business. Retrieved 3 March 2013.
- ^ "Smog war casualty: China coal city bears brunt of pollution crackdown". Reuters. 27 November 2018.
- ^ "Direct Liquefaction Processes". National Energy Technology Laboratory. Archived from the original on 25 July 2014. Retrieved 16 July 2014.
- ^ Liu, Weiguo; Wang, Jingxin; Bhattacharyya, Debangsu; Jiang, Yuan; Devallance, David (2017). "Economic and environmental analyses of coal and biomass to liquid fuels". Energy. 141: 76–86. Bibcode:2017Ene...141...76L. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2017.09.047.
- ^ "CHN Energy to build new coal-to-liquid production lines". Xinhua News Agency. 13 August 2018.
- ^ "New IMSBC Code requirements aim to control liquefaction of coal cargoes". Hellenic Shipping News Worldwide. 29 November 2018. Archived from the original on 3 August 2020. Retrieved 1 December 2018.
- ^ "Conversion of Methanol to Gasoline". National Energy Technology Laboratory. Archived from the original on 17 July 2014. Retrieved 16 July 2014.
- ^ "Sasol Is Said to Plan Sale of Its South Africa Coal Mining Unit". Bloomberg.com. 18 September 2019. Retrieved 31 May 2020.
- ^ "Coal mining". World Coal Association. 28 April 2015. Retrieved 5 December 2018.
- ^ "Coal industry faces 1 million job losses from global energy transition - research". Reuters. 10 October 2023.
- ^ "China: seven miners killed after skip plummets down mine shaft". The Guardian. Agence France-Presse. 16 December 2018.
- ^ "The One Market That's Sure To Help Coal". Forbes. 12 August 2018.
- ^ "BP Statistical review of world energy 2016" (XLS). British Petroleum. Archived from the original on 2 December 2016. Retrieved 8 February 2017.
- ^ a b c "Trade – Coal 2023 – Analysis". IEA. Retrieved 28 October 2024.Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
- ^ "Coal 2017" (PDF). IEA. Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 June 2018. Retrieved 26 November 2018.
- ^ "Coal Prices and Outlook". U.S. Energy Information Administration.
- ^ "New wind and solar generation costs fall below existing coal plants". Financial Times. Retrieved 8 November 2018.
- ^ "Lazard's Levelized Cost of Energy ('LCOE') analysis – Version 12.0" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 November 2018. Retrieved 9 November 2018.
- ^ a b c "40% of China's coal power stations are losing money". Carbon Tracker. 11 October 2018. Retrieved 11 November 2018.
- ^ "Economic and financial risks of coal power in Indonesia, Vietnam and the Philippines". Carbon Tracker. Retrieved 9 November 2018.
- ^ "India's Coal Paradox". 5 January 2019.
- ^ Pukowiec-Kurda, Katarzyna; Apollo, Michal (27 August 2024). "From coal to tourism: a game-changer in the sustainable transition process". Journal of Tourism Futures. doi:10.1108/JTF-05-2024-0086. ISSN 2055-5911.
- ^ "Consumption – Coal Information: Overview – Analysis". IEA. Retrieved 28 October 2024.Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
- ^ "Coal 2018:Executive Summary". International Energy Agency. 2018. Archived from the original on 18 December 2018. Retrieved 18 December 2018.
- ^ Ritchie, Hannah; Roser, Max (2021). "What are the safest and cleanest sources of energy?". Our World in Data. Archived from the original on 15 January 2024. Data sources: Markandya & Wilkinson (2007); UNSCEAR (2008; 2018); Sovacool et al. (2016); IPCC AR5 (2014); Pehl et al. (2017); Ember Energy (2021).
- ^ Toxic Air: The Case for Cleaning Up Coal-fired Power Plants. American Lung Association (March 2011) Archived 26 January 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b Hendryx, Michael; Zullig, Keith J.; Luo, Juhua (8 January 2020). "Impacts of Coal Use on Health". Annual Review of Public Health. 41: 397–415. doi:10.1146/annurev-publhealth-040119-094104. ISSN 0163-7525. PMID 31913772.
- ^ "Health". Endcoal. Archived from the original on 22 December 2017. Retrieved 3 December 2018.
- ^ a b "India shows how hard it is to move beyond fossil fuels". The Economist. 2 August 2018.
- ^ Preventing disease through healthy environments: a global assessment of the burden of disease from environmental risks Archived 30 July 2016 at the Wayback Machine. World Health Organization (2006)
- ^ Global Health Risks: Mortality and Burden of Disease Attributable to Selected Major Risks (PDF). World Health Organization. 2009. ISBN 978-92-4-156387-1. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 February 2012.
- ^ "WHO – Ambient (outdoor) air quality and health". who.int. Archived from the original on 4 January 2016. Retrieved 7 January 2016.
- ^ "Global SO2 emission hotspot database" (PDF). Greenpeace. August 2019. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 October 2019.
- ^ Coal Pollution Damages Human Health at Every Stage of Coal Life Cycle, Reports Physicians for Social Responsibility Archived 31 July 2015 at the Wayback Machine. Physicians for Social Responsibility. psr.org (18 November 2009)
- ^ Burt, Erica; Orris, Peter and Buchanan, Susan (April 2013) Scientific Evidence of Health Effects from Coal Use in Energy Generation Archived 14 July 2015 at the Wayback Machine. University of Illinois at Chicago School of Public Health, Chicago, Illinois, US
- ^ "The Unpaid Health Bill – How coal power plants make us sick". Health and Environment Alliance. 7 March 2013. Retrieved 15 December 2018.
- ^ "Coal in China: Estimating Deaths per GW-year". Berkeley Earth. 18 November 2016. Retrieved 1 February 2020.
- ^ "Health benefits will offset cost of China's climate policy". MIT. 23 April 2018. Retrieved 15 December 2018.
- ^ Beach, Brian; Hanlon, W. Walker (2018). "Coal Smoke and Mortality in an Early Industrial Economy". The Economic Journal. 128 (615): 2652–2675. doi:10.1111/ecoj.12522. ISSN 1468-0297. S2CID 7406965.
- ^ "Black Lung Disease-Topic Overview". WebMD. Archived from the original on 10 July 2015.
- ^ "Black Lung". umwa.org. Archived from the original on 3 February 2016. Retrieved 7 January 2016.
- ^ World Coal Association "Environmental impact of Coal Use" Archived 23 February 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Coal". U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. 5 February 2014. Archived from the original on 20 July 2015.
- ^ "Coal Ash: Toxic – and Leaking". psr.org. Archived from the original on 15 July 2015.
- ^ Hvistendahl, Mara (13 December 2007). "Coal Ash Is More Radioactive than Nuclear Waste". Scientific American. Archived from the original on 10 July 2015.
- ^ "Coal and the environment". U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). Retrieved 27 January 2023.
- ^ Zagoruichyk, Anastasiia (6 July 2022). "Emissions from mining cause 'up to £2.5tn' in environmental damages each year". Carbon Brief. Retrieved 27 January 2023.
- ^ Tiwary, R. K. (2001). "Environmental Impact of Coal Mining on Water Regime and Its Management". Water, Air, & Soil Pollution. 132: 185–99. Bibcode:2001WASP..132..185T. doi:10.1023/a:1012083519667. S2CID 91408401.
- ^ "Pakistan's Coal Trap". Dawn. 4 February 2018.
- ^ Zhong, Qirui; Shen, Huizhong; Yun, Xiao; Chen, Yilin; Ren, Yu'ang; Xu, Haoran; Shen, Guofeng; Du, Wei; Meng, Jing; Li, Wei; Ma, Jianmin (2 June 2020). "Global Sulfur Dioxide Emissions and the Driving Forces". Environmental Science & Technology. 54 (11): 6508–6517. Bibcode:2020EnST...54.6508Z. doi:10.1021/acs.est.9b07696. ISSN 0013-936X. PMID 32379431. S2CID 218556619.
- ^ Barrie, L.A.; Hoff, R.M. (1984). "The oxidation rate and residence time of sulphur dioxide in the arctic atmosphere". Atmospheric Environment. 18 (12): 2711–2722. Bibcode:1984AtmEn..18.2711B. doi:10.1016/0004-6981(84)90337-8.
- ^ Human Impacts on Atmospheric Chemistry, by PJ Crutzen and J Lelieveld, Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, Vol. 29: 17–45 (Volume publication date May 2001)
- ^ Cray, Dan (23 July 2010). "Deep Underground, Miles of Hidden Wildfires Rage". Time. Archived from the original on 28 July 2010.
- ^ "Das Naturdenkmal Brennender Berg bei Dudweiler" [The natural monument Burning Mountain in Dudweiler]. Mineralienatlas (in German). Retrieved 3 October 2016.
- ^ "World Of Coke: Coke is a High Temperature Fuel". www.ustimes.com. Archived from the original on 27 November 2015. Retrieved 16 January 2016.
- ^ Rajaram, Vasudevan; Parameswaran, Krishna; Dutta, Subijoy (2005). Sustainable Mining Practices: A Global Perspective. CRC Press. p. 113. ISBN 978-1-4398-3423-7.
- ^ "The NOAA Annual Greenhouse Gas Index (AGGI)". NOAA.gov. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). 2024. Archived from the original on 5 October 2024.
- ^ a b c Gençsü (2019), p. 8
- ^ "China's Coal Plants Haven't Cut Methane Emissions as Required, Study Finds". The New York Times. 29 January 2019.
- ^ Gabbatiss, Josh (24 March 2020). "Coal mines emit more methane than oil-and-gas sector, study finds". Carbon Brief. Retrieved 29 March 2020.
- ^ "Emissions". Global Carbon Atlas. Retrieved 6 November 2018.
- ^ "How much carbon dioxide is produced when different fuels are burned?". eia.gov. Archived from the original on 12 January 2016. Retrieved 7 January 2016.
- ^ Tranberg, Bo; Corradi, Olivier; Lajoie, Bruno; Gibon, Thomas; Staffell, Iain; Andresen, Gorm Bruun (2019). "Real-Time Carbon Accounting Method for the European Electricity Markets". Energy Strategy Reviews. 26: 100367. arXiv:1812.06679. Bibcode:2019EneSR..2600367T. doi:10.1016/j.esr.2019.100367. S2CID 125361063.
- ^ Vidal, John; Readfearn, Graham (18 November 2013). "Leave coal in the ground to avoid climate catastrophe, UN tells industry". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 2 January 2017.
- ^ "We have too many fossil-fuel power plants to meet climate goals". Environment. 1 July 2019. Archived from the original on 2 July 2019. Retrieved 30 September 2019.
- ^ "Sino German Coal fire project". Archived from the original on 30 August 2005. Retrieved 9 September 2005.
- ^ "Committee on Resources-Index". Archived from the original on 25 August 2005. Retrieved 9 September 2005.
- ^ "Snapshots 2003" (PDF). fire.blm.gov. Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 February 2006. Retrieved 9 September 2005.
- ^ "EHP 110-5, 2002: Forum". Archived from the original on 31 July 2005. Retrieved 9 September 2005.
- ^ "Overview about ITC's activities in China". Archived from the original on 16 June 2005. Retrieved 9 September 2005.
- ^ "The Niederraussem Coal Innovation Centre" (PDF). RWE. Archived (PDF) from the original on 22 July 2013. Retrieved 21 July 2014.
- ^ Kazlou, Tsimafei; Cherp, Aleh; Jewell, Jessica (October 2024). "Feasible deployment of carbon capture and storage and the requirements of climate targets". Nature Climate Change. 14 (10): 1047–1055, Extended Data Fig. 1. doi:10.1038/s41558-024-02104-0. ISSN 1758-6798. PMC 11458486.
- ^ "Net Zero Roadmap: A Global Pathway to Keep the 1.5 °C Goal in Reach – Analysis". IEA. 26 September 2023. Retrieved 11 September 2024.
- ^ "Global Status Report 2024". Global CCS Institute. pp. 57–58. Retrieved 19 October 2024.
- ^ Grandia, Kevin (9 December 2008). "Give the gift of Asthma and a Warmer Planet this Christmas". DeSmog. Retrieved 2 November 2024.
- ^ a b c d e McDonald, Jessica (9 November 2018). "Clearing Up the Facts Behind Trump's 'Clean Coal' Catchphrase". FactCheck.org. Retrieved 30 October 2024.
- ^ a b c Khourdajie, Alaa Al; Bataille, Chris; Nilsson, Lars J. (13 December 2023). "The COP28 climate agreement is a step backwards on fossil fuels". The Conversation. Retrieved 1 October 2024.
- ^ "WGIII Summary for Policymakers Headline Statements". Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. 4 April 2022. Retrieved 2 October 2024.
- ^ Staff, Carbon Brief (5 December 2023). "Q&A: Why defining the 'phaseout' of 'unabated' fossil fuels is so important at COP28". Carbon Brief. Retrieved 2 October 2024.
- ^ "World Energy Investment 2019" (PDF). webstore.iea.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 June 2020. Retrieved 14 July 2019.
- ^ Carrington, Damian (10 December 2018). "Tackle climate or face financial crash, say world's biggest investors". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 22 July 2019.
- ^ Kompas, Tom; Pham, Van Ha; Che, Tuong Nhu (2018). "The Effects of Climate Change on GDP by Country and the Global Economic Gains From Complying With the Paris Climate Accord". Earth's Future. 6 (8): 1153–1173. Bibcode:2018EaFut...6.1153K. doi:10.1029/2018EF000922. hdl:1885/265534. ISSN 2328-4277.
- ^ "Labor opposes plan to indemnify new coal plants and warns it could cost billions". The Guardian. 24 October 2018.
- ^ "Superfund Scandal Leads to Prison Time for Coal Lobbyist, Lawyer". Sierra Club. 24 October 2018.
- ^ Ricke, Katharine; Drouet, Laurent; Caldeira, Ken; Tavoni, Massimo (2018). "Country-level social cost of carbon". Nature Climate Change. 8 (10): 895–900. Bibcode:2018NatCC...8..895R. doi:10.1038/s41558-018-0282-y. hdl:11311/1099986. S2CID 135079412.
- ^ Jha, Akshaya; Muller, Nicholas Z. (2018). "The local air pollution cost of coal storage and handling: Evidence from U.S. power plants". Journal of Environmental Economics and Management. 92: 360–396. Bibcode:2018JEEM...92..360J. doi:10.1016/j.jeem.2018.09.005. S2CID 158803149.
- ^ "The human cost of coal in the UK: 1600 deaths a year". New Scientist. Archived from the original on 24 April 2015.
- ^ "Environmentalism". The Economist. 4 February 2014. Archived from the original on 28 January 2016. Retrieved 7 January 2016.
- ^ "Air Pollution and Health in Bulgaria" (PDF). HEAL. Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 December 2015. Retrieved 26 October 2018.
- ^ Sun, Dong; Fang, Jing; Sun, Jingqi (2018). "Health-related benefits of air quality improvement from coal control in China: Evidence from the Jing-Jin-Ji region". Resources, Conservation and Recycling. 129: 416–423. Bibcode:2018RCR...129..416S. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2016.09.021.
- ^ "Support for fossil fuels almost doubled in 2021, slowing progress toward international climate goals, according to new analysis from OECD and IEA - OECD". www.oecd.org. Retrieved 27 September 2022.
- ^ "MANAGING THE PHASE-OUT OF COAL A COMPARISON OF ACTIONS IN G20 COUNTRIES" (PDF). Climate Transparency. May 2019. Archived (PDF) from the original on 24 May 2019.
- ^ "Deal reached on EU energy market design, incl end of coal subsidies License: CC0 Creative Commons". Renewables Now. 19 December 2018.
- ^ "Regional Briefings for the 2018 Coal Plant Developers List" (PDF). Urgewald. Retrieved 27 November 2018.
- ^ "The World Needs to Quit Coal. Why Is It So Hard?". The New York Times. 24 November 2018. Archived from the original on 1 January 2022.
- ^ "Fossil-fuel subsidies". IEA. Retrieved 16 November 2018.
- ^ "Turkey". Ember. 28 March 2021. Archived from the original on 27 October 2021. Retrieved 9 October 2021.
- ^ "Regional Briefings for the 2018 Coal Plant Developers List" (PDF). Urgewald. Retrieved 27 November 2018.
- ^ "'Stranded' fossil fuel assets may prompt $4 trillion crisis". Cosmos. 4 June 2018. Retrieved 30 September 2019.
- ^ Carrington, Damian (8 September 2021). "How much of the world's oil needs to stay in the ground?". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 8 September 2021. Retrieved 10 September 2021.
- ^ Welsby, Dan; Price, James; Pye, Steve; Ekins, Paul (8 September 2021). "Unextractable fossil fuels in a 1.5 °C world". Nature. 597 (7875): 230–234. Bibcode:2021Natur.597..230W. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03821-8. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 34497394.
- ^ "5 Asian countries building 80% of new coal power – Carbon Tracker".
- ^ "EGEB: 76% of proposed coal plants have been canceled since 2015". 14 September 2021.
- ^ "Pacific nations under climate threat urge Australia to abandon coal within 12 years". The Guardian. 13 December 2018.
- ^ Fiona, Harvey (21 May 2021). "Richest nations agree to end support for coal production overseas". The Guardian. Retrieved 22 May 2021.
- ^ "Kentucky: Secretary of State – State Mineral". 20 October 2009. Archived from the original on 27 May 2011. Retrieved 7 August 2011.
- ^ "Utah State Rock – Coal". Pioneer: Utah's Online Library. Utah State Library Division. Archived from the original on 2 October 2011. Retrieved 7 August 2011.
- ^ "WVGES Frequently Asked Questions". www.wvgs.wvnet.edu. Retrieved 25 September 2023.
- ^ Jack, Lauren (20 December 2022). "What is First Footing? Where the Scottish Hogmanay tradition comes from and common first footing gifts". scotsman.com. National World Publishing, LTD. Retrieved 21 November 2024.
Further reading
- Freese, Barbara (2003). Coal: A Human History. Penguin Books. ISBN 978-0-7382-0400-0. OCLC 51449422.
- Thurber, Mark (2019). Coal. Polity Press. ISBN 978-1509514014.
- Paxman, Jeremy (2022). Black Gold : The History of How Coal Made Britain. William Collins. ISBN 9780008128364.
External links
- Coal Transitions
- Coal – International Energy Agency
- CoalExit
- European Association for Coal and Lignite
- Coal news and industry magazine
- Global Coal Plant Tracker
- Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air
- . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 6 (11th ed.). 1911. pp. 574–93.
- . New International Encyclopedia. 1905.
- . Collier's New Encyclopedia. 1921.


